BIOMEDICAL STATISTICS TUTORIAL
Meta-analysis is one of the concepts of scientific methodology, and is a frequent but optional component of systematic reviews of empirical research. It joins the results of several scientific studies and tests one or more interrelated scientific hypotheses using quantitative (statistical) methods. This analysis can either use primary data from the original studies or published (secondary) results of studies dealing with the same problem. Meta-analysis is used to obtain an estimate of the magnitude of an unknown effect, and compare the results of different studies, identifying patterns or other relationships in them, as well as possible sources of disagreement. Meta-analyses are the highest level of credibility within evidence-based medicine (EBM), so meta-analysis results are considered as the most reliable source of evidence. Understanding all the procedures of a meta-analysis will allow researchers to analyze the results of such studies correctly, as well as formulate tasks when conducting meta-analyses on their own. In this article the reader will be introduced to key concepts such as weighted effects, heterogeneity, the different types of statistical models used, and how to work with some of the types of plots produced in meta-analyses.
INTERNAL MEDICINE
Aim. The aim of this study was to analyze eating behavior and leptin receptor (LEPR) gene in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D).
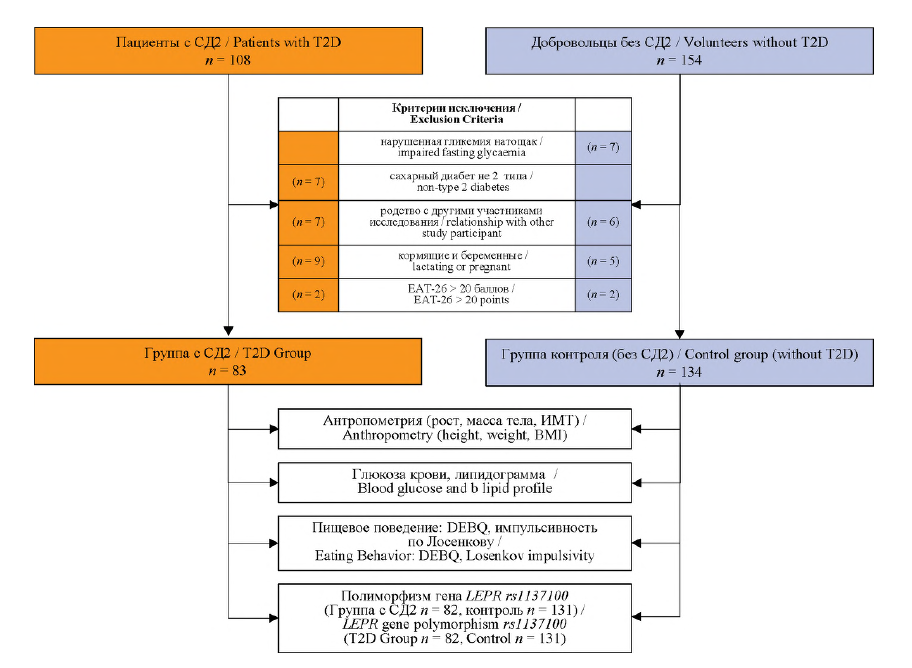
Materials and methods. 83 patients with T2D (62 women, 21 men) aged 59.0 ± 9.9 years and 134 people without clinical and laboratory signs of diabetes mellitus (105 women, 29 men) aged 55.0 ± 10.2 years were examined. Bulimia nervosa was excluded in all the patients. Eating behavior was assessed using Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire, V.A. Losenkov’s
Impulsivity Questionnaire. Genotyping of the LEPR gene rs1137100 marker was performed using polymerase chain reaction. The Mann-Whitney U-test and Pearson chi-square were used to compare the values of the variables; ROC-analysis was performed.
Results. The emotional eating was more pronounced in T2D group (4.9 (4.1; 5.2) vs 3.1 (2.8; 3.8), p < 0.0001), but the restrained (2.8 (2.6; 3.6) vs 3.3 (2.6; 4.2), p < 0.0001) and external eating was less pronounced (3.3 (3.0; 3.8) vs 3.8 (3.3; 4.4), p < 0.0001), T2D patients were also less impulsive (47 (38; 66) vs 61 (54.5; 70), p < 0.0001). These differences for emotional eating are confirmed in both subgroup of excess body weight and in subgroups of all degrees of obesity. The best predictive model of T2D was obtained for emotional eating with a cut-off point 4.1 scores: sensitivity 74.7 %, specificity 79.1 %, AUROC = 0.777; 95 % confidence interval: 0.715–0.830, p < 0.0001. The distribution of genotypes by the polymorphic marker rs1137100 of the LEPR gene was similar in both groups. Restrictive eating was lower in patients with GG genotype compared to AA and GA (1.77 ± 0.52 vs 2.94 ± 0.08, p < 0.01).
Conclusion. Рatients with T2D are characterized by emotional eating behavior. The association of the polymorphic locus rs1137100 of the LEPR gene with restrained eating behavior in T2D suggests the presence of genetic factors for the formation of eating patterns.
Aim. To study in real clinical practice extrapulmonary personalized factors in patients with asthma depending on the presence or absence of obesity and to build a model of asthma control based on them.
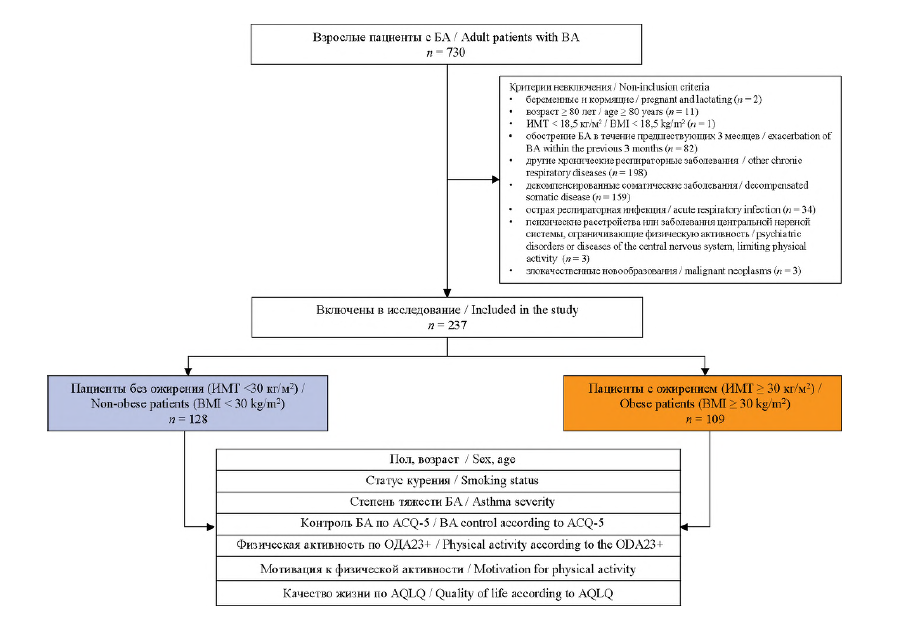
Materials and methods. Cross-sectional study was performed in 7 outpatient centers and included 237 adult patients with bronchial asthma (mean age 52.6 ± 1.3 years). The patients were divided in groups according to body mass index (BMI): without obesity (BMI < 30 kg/m2) – 128 patients, with obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) – 109 patients. Asthma control was assessed by Asthma Control Questionnaire-5, physical activity – by the motor activity questionnaire (ODA23+), physical activity motivation – by data from the questionnaire. A linear regression model was built with the inclusion of sex, smoking, BMI, physical activity to predict the level of asthma control. Elasticity coefficient Ej, β- and Δ-coefficients and their ranks were calculated.
Results. The distribution of patients according to the degree of asthma control differed statistically significantly in the groups: controlled, partially controlled and uncontrolled were 25.8 %, 60.2 %, 14 % and 0 %, 33.9 %, 66.1 %, respectively, in groups without obesity and obese (p < 0.001). High or moderate physical activity was present in 88 % of non-obese and 47% of obese patients (p < 0.05). No differences were found in the motivation for physical activity: 41% with obesity and 42 % without obesity belonged to the category of “thinking about or trying to exercise”. In the regression model, the ranks were distributed as follows (the sum of the ranks of the coefficients Ej, β, and Δ is calculated) rank 1 – BMI (0.8857, 0.4163, 0.5429), rank 2 – level of physical activity (0.6489, 0.3497, 0.4467), rank 3 – smoking status (0.0339, 0.1333, 0.0047). The coefficient of the model was not significant for sex.
Conclusion. Obesity and low physical activity are the main personalized extrapulmonary factors that affect control of asthma. A significant part of the patients are motivated to modify their level of physical activity.
MODELING IN MEDICINE
Aim. Develop a neural network to build 3D models of kidney neoplasms and adjacent structures.
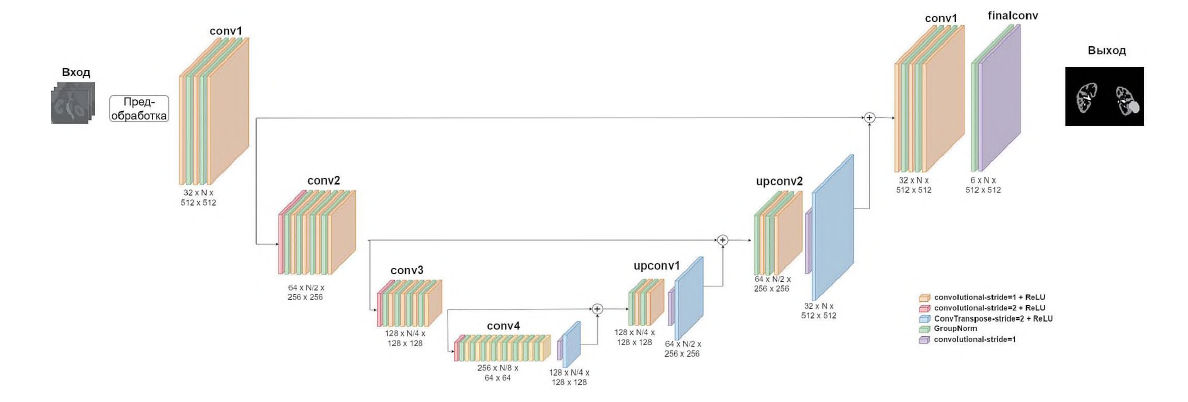
Materials and methods. DICOM data (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine standard) from 41 patients with kidney neoplasms were used. Data included all phases of contrast-enhanced multispiral computed tomography. We split the data: 32 observations for the training set and 9 – for the validation set. At the labeling stage, the arterial, venous, and excretory phases were taken, affine registration was performed to jointly match the location of the kidneys, and noise was removed using a median filter and a non-local means filter. Then the masks of arteries, veins, ureters, kidney parenchyma and kidney neoplasms were marked. The model was the SegResNet architecture. To assess the quality of segmentation, the Dice score was compared with the AHNet, DynUNet models and with three variants of the nnU-Net (lowres, fullres, cascade) model.
Results. On the validation subset, the values of the Dice score of the SegResNet architecture were: 0.89 for the normal parenchyma of the kidney, 0.58 for the kidney neoplasms, 0.86 for arteries, 0.80 for veins, 0.80 for ureters. The mean values of the Dice score for SegResNet, AHNet and DynUNet were 0.79; 0.67; and 0.75, respectively. When compared with the nnU-Net model, the Dice score was greater for the kidney parenchyma in SegResNet – 0.89 compared to three model variants: lowres – 0.69, fullres – 0.70, cascade – 0.69. At the same time, for the neoplasms of the parenchyma of the kidney, the Dice score was comparable: for SegResNet – 0.58, for nnU-Net fullres – 0.59; lowres and cascade had lower Dice score of 0.37 and 0.45, respectively.
Conclusion. The resulting SegResNet neural network finds vessels and parenchyma well. Kidney neoplasms are more difficult to determine, possibly due to their small size and the presence of false alarms in the network. It is planned to increase the sample size to 300 observations and use post-processing operations to improve the model.
NEUROSURGERY
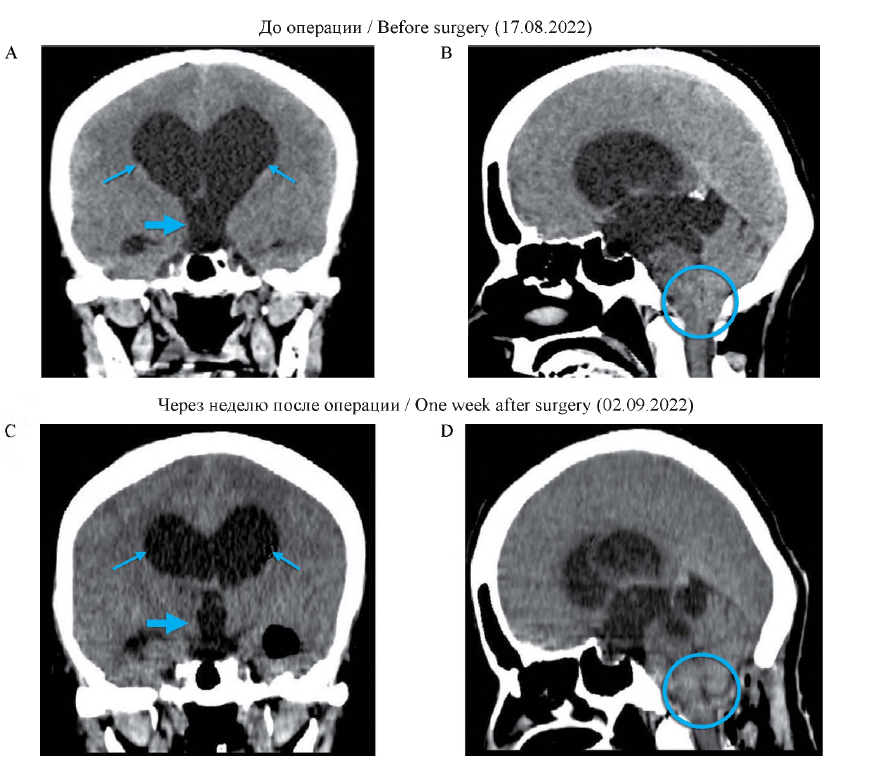
Treatment of patients with the simultaneous presence of Chiari malformation type I (MC I) and hydrocephalus may include both one-stage and two-stage surgical interventions. The article describes the two-stage surgical treatment experience performed for the first time in the Republic of Tajikistan.
Description of the case. A 50-year-old female patient with a three-year history of bursting headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting developed impaired coordination of movements and decreased visual acuity. Computed tomography (CT) revealedsigns of MC I: descent of the cerebellar tonsils 5 mm below the level of the foramen magnum and occlusive triventricular hydrocephalus with symmetrical enlargement of the lateral and third ventricles. The patient underwent surgery – endoscopic third ventriculocisternostomy (ETV) in combination with decompressive suboccipital craniectomy, which was supplemented by CI laminectomy. After the surgery, the symptoms regressed. According to the control CT scan, there was a moderate decrease in the size of the lateral and third ventricles, restoration of the normal anatomical structure of the posterior cranial fossa.
ISSN 2658-3348 (Online)