CELL BIOLOGY, CYTOLOGY, HISTOLOGY
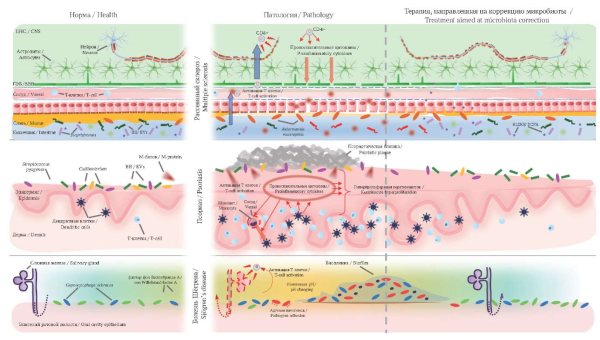
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by dysregulation of immune responses and damage to healthy body tissues. Their complete cure remains elusive, and existing therapies are often accompanied by side effects. Recent studies have shown a signifi cant role of disturbances in the composition of the microbiome in the development of autoimmune reactions. Moreover, modulation of the microbiome through various therapeutic interventions represents a promising direction in the framework of complex therapy of the underlying disease. Extracellular vesicles, in particular exosomes, transport biologically active substances between cells, and a number of studies have shown their therapeutic effect in autoimmune diseases. However, the role of extracellular vesicles in modulating the microbiome remains poorly understood, and further research is needed to better understand their impact on the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and associated microbiome changes, as well as to develop new treatment strategies. The presented literature review, based on a study of English-language sources, examines the importance of the microbiota of different loci of the human body (intestines, skin, oral cavity) in the development of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, psoriasis and Sjögren’s disease. The role of extracellular vesicles in modulating the microbiome during autoimmune diseases therapy is discussed.
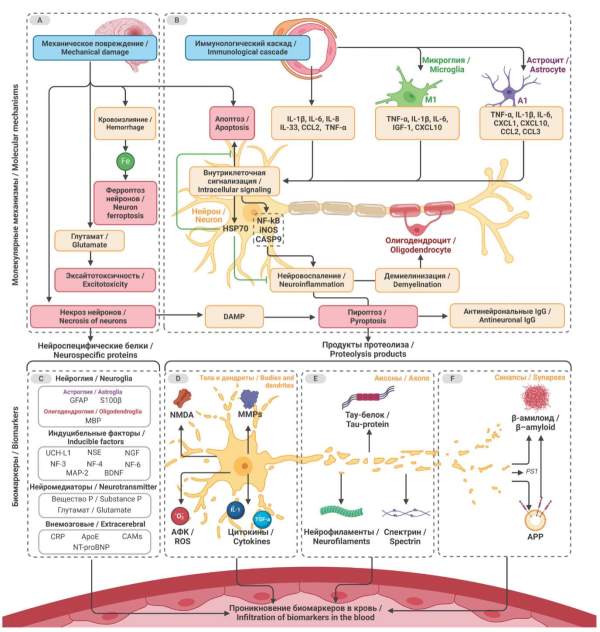
Inflammatory processes accompanied by damage to the cell bodies of neurons are combined into the group of neuroinflammation. At the molecular, cellular and tissue levels, neuroinflammation serves as a sanogenetic response to a variety of injuries, including post-traumatic conditions and neurodegeneration. However, inflammatory changes in long-lived cells such as neurons inevitably trigger a range of adverse effects. As a result, prognosis often depends on the severity of neuroinflammation. In this work, we review the spectrum of biomarkers involved in two key mechanisms of neuroinflammation: immune-mediated and mechanical injury, that have a potential clinical application: cytokines, neurospecific proteins and their proteolysis products, markers of oxidative stress, matrix metalloproteinases and endocrine parameters. Over the past decades, a significant pool of data on neuroinflammation biomarkers has been accumulated and continues to grow, but no consensus has been reached on the actual gradation of their clinical significance. Applied branches of medicine require further systematization of information on biomarkers of neuroinflammation for effective prognostic decisions.
PATHOLOGICAL PHYSIOLOGY
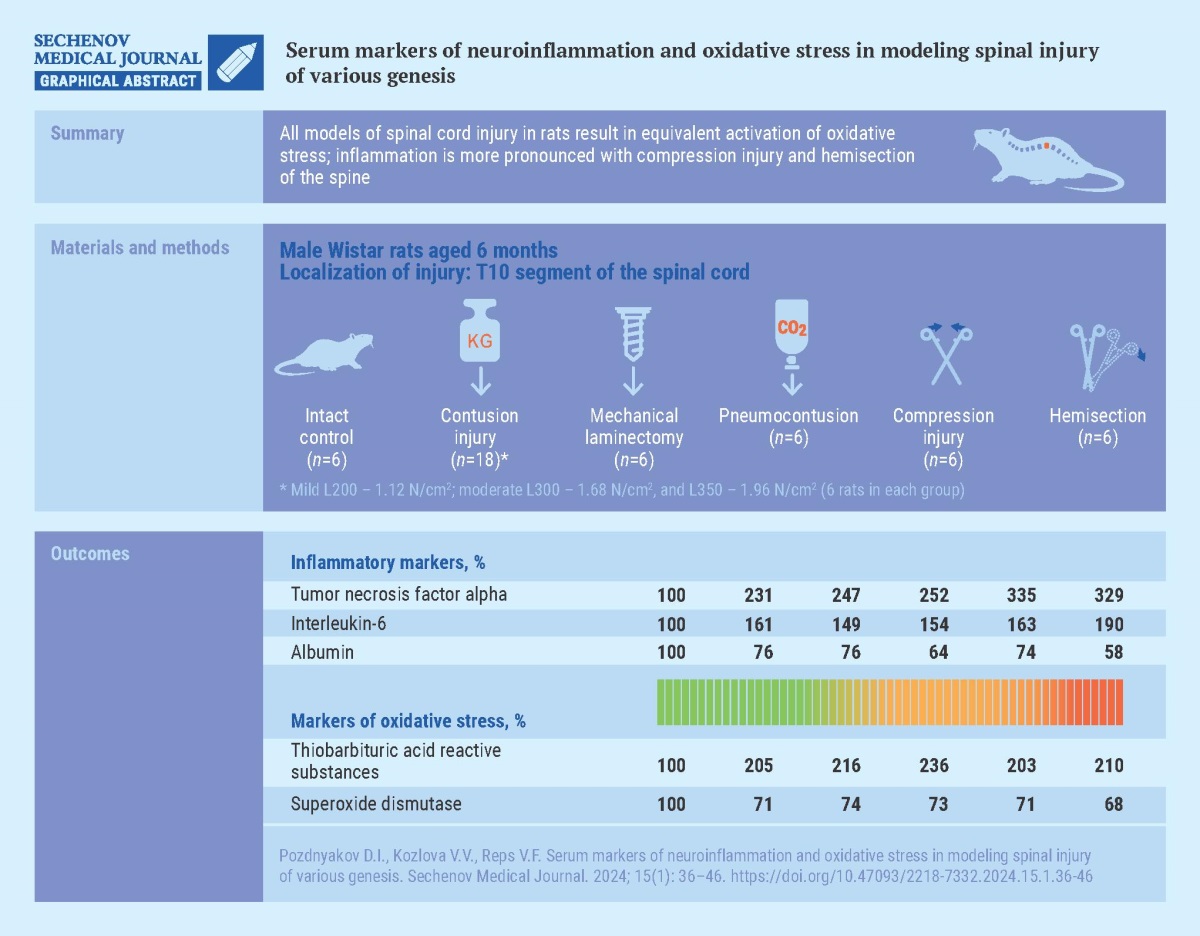
Aim. To evaluate changes in the concentration of molecules that mark the neurodegenerative process, experimental spinal cord injuries (SCI) of various origins were studied.
Materials and methods. SCI was modeled in six-month-old male Wistar rats by exposing the T10 vertebra to: carbon dioxide under a pressure of 2 N/cm2 (pneumocontusion); free-falling load of three weights of 1.12 N/cm2, 1.68 N/cm2, 1.96 N/cm2 (contusion injury); compression with forceps (compression injury); partial hemisection of the spinal cord; mechanical laminectomy using a mechanical drill. There were 6 rats in each group, including the intact control group. On the 28th day after a single application of SCI in rats, the concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), albumin, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBA-RS) and superoxide dismutase activity were assessed in the blood serum.
Results. When modeling SCI of various origins in rats, the serum concentration of TNF-α increased (from 115.5% (p < 0.05) in mild contusion to 234.5% (p < 0.05) in compression trauma compared to intact control) as well as IL-6 (from 49.2% (p < 0.05) in mechanical laminectomy to 89.8% (p < 0.05) in hemisection compared with intact control), suggesting activation of inflammatory reactions. The concentration of albumin in the blood serum of rats with SCI was lower than that of intact animals, especially in the hemisection group – by 41.9% (p < 0.05). Animals with SCI had an increase in TBA-RS concentration ranging from 103.2% (p < 0.05) in mild contusion and compression to 135.5% (p < 0.05) in pneumocontusion, and a decrease in superoxide dismutase activity ranging from 26.3% (p < 0.05) in laminectomy to 31.7% (p < 0.05) in hemisection. At the same time, injuries caused by spinal compression and hemisection led to a more pronounced activation of the inflammatory process, as evidenced by the increased TNF-α content compared to other variants of SCI modeling.
Conclusion. All SCI simulations resulted in equivalent activation of oxidative stress, while inflammation is more pronounced when reproducing compression injury and injury caused by spinal hemisection.
MODELING IN MEDICINE
Aim. To develop a biomechanical model of the knee joint, including a detailed representation of the patellofemoral segment for the normal anatomy of bones, joints, ligaments and muscles, and study patellar movement during passive knee flexion.
Materials and methods. The architecture of the biomechanical model was developed using an open source software system for biomechanical modeling OpenSim. Patellofemoral joint with 6 degrees of freedom, patellar stabilizers – medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL), medial patellotibial ligament (MPTL), lateral retinaculum (LR), and patellar contact surfaces (facets) were included in the model. Gmsh and Paraview were used to generate the contact surfaces. Simulations of knee passive flexion with consistent patellar stabilizers exclusion were carried out to identify their influence on patellar movement.
Results. The presented biomechanical model provides a detailed analysis of the normal dynamics of the patella and the role of different anatomical structures in its functioning and can be used for further experiments investigating of the patellar movement. The experiment involving all ligaments is consistent with the physiological norm. Disabling MPTL has minimal effects on patellar tilt and translation, which aligns with its small size. In contrast, deactivating MPFL results in increased lateral tilt and translation of the patella. Additionally, deactivation of LR components 1 and 2 induces more medial tilt and translation. Deactivating LR components 3 and 4 leads to further lateral translation and slight additional medial tilt.
Conclusion. Computational results show that all ligaments contribute to the normal movement of the patella. These findings highlight the importance of stabilizing structures in maintaining patellar stability during knee flexion.
Aim. The aim of this study was to develop and evaluate the effectiveness of a convolutional neural network (CNN) in detecting papillary bladder cancer (PBC) using a limited set of cystoscopic images.
Materials and methods. Twenty patients who underwent white light cystoscopy and histologically confirmed papillary bladder cancer were included in the study. The dataset included 125 images retrieved and marked by a urologist: 88 images were papillary tumors and 37 were healthy bladder wall tissue. 100 images were selected for training and 25 images were selected for validation. The U-net architecture and the CNN VGG16 model were used. A binary mask was manually created for each image based on the comments given by the urologist. Each image was additionally processed for model compatibility, with 224×224 pixel images as input to reduce the number of parameters. The dataset was augmented by applying vertical and horizontal turns, as well as random rotations. The following metrics were calculated: Dice coefficient, sensitivity, specificity, proportion of false positives and false negatives, accuracy, and area under the ROC curve.
Results. The original data set yielded the following parameters: specificity 84.56%, sensitivity 82.18%, false positive rate 15.44%, false negative rate 17.82%, accuracy 76.40%, and a Dice coefficient 83.16%. For the augmented dataset, the following values were obtained: specificity: 82.99%, sensitivity: 82.70%, false positive rate 17.01%, false negative rate 17.30%, accuracy 74.72%, Dice coefficient – 82.82%. The area under the ROC curves was 92.93% for the original dataset and 91.69% for the augmented dataset.
Conclusion. The CNN created in this study can detect signs of early PBC when analyzing cystoscopic images. The results of the study can be a starting point for developing new methods to diagnose PBC using deep learning technologies.
ISSN 2658-3348 (Online)