INTERNAL MEDICINE
Aim. To study the prevalence of pneumonia features associated with 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in cancer patients based on chest computed tomography (CT) data using an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm.
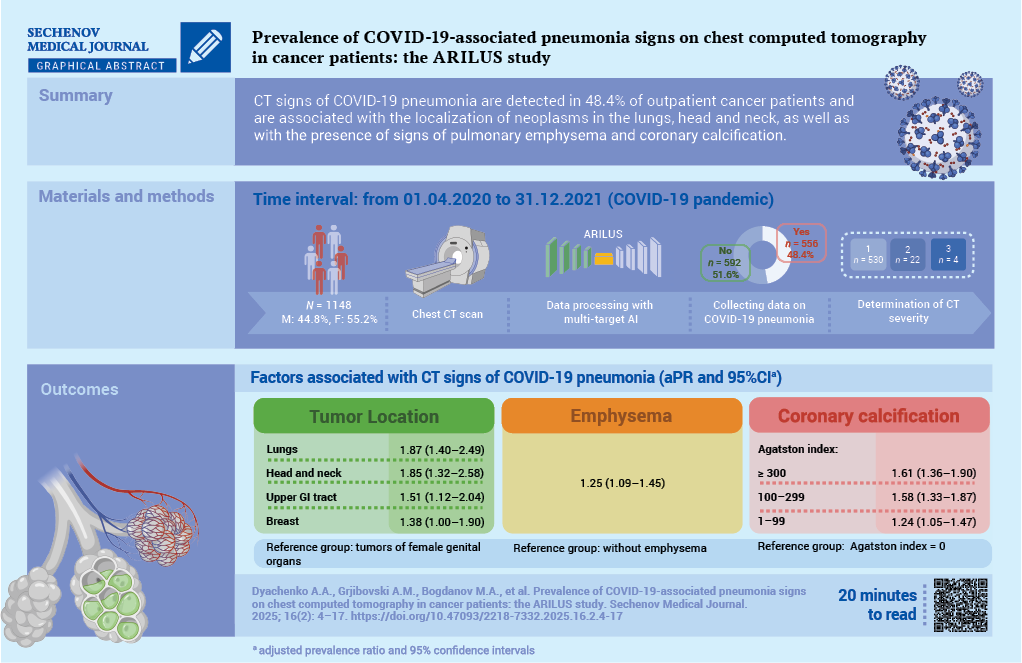
Materials and methods. A cross-sectional study was conducted as part of the ARILUS project. Using multitarget AI, CT images of 1148 patients examined at the Arkhangelsk Clinical Oncology Dispensary from 01.04.2020 to 31.12.2021 were analyzed. Patients were divided into groups: without signs of pneumonia (n = 592, 51.6%) and with signs of pneumonia (n = 556, 48.4%). In 95.3% of patients with pneumonia, the lesion volume was less than 25% (CT-1). Using multivariate Poisson regression, adjusted prevalence ratios (aPR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated.
Results. For demographic characteristics such as gender, age, place of residence, no relationship with the presence of signs of COVID-19 pneumonia was established. Topography of neoplasm is associated with the presence of signs of COVID-19 pneumonia (reference group – cancers of the female genital organs): lung cancer – aPR 1.87; 95% CI: 1.40–2.49; head and neck cancers – aPR 1.85; 95% CI: 1.32–2.58; upper gastrointestinal tract – aPR 1.51; 95% CI: 1.12–2.04; breast cancer – aPR: 1.38; 95% CI: 1.00–1.90; p < 0.01. The presence of pulmonary emphysema is associated with signs of COVID-19 pneumonia: aPR 1.25; 95% CI: 1.09–1.45, p = 0.002. With an increase in the Agatston score (AS) reflecting coronary artery calcification (reference group absence of calcification), the association with the presence of signs of COVID-19 pneumonia increased – for AS 1–99: aPR 1.24; 95% CI: 1.05–1.47; AS 100– 299: aPR 1.58; 95% CI: 1.33–1.87; AS 300 and above: aPR 1.61; 95% CI: 1.36–1.90; p < 0.001 for a linear trend.
Conclusion. Factors associated with the detection of COVID-19 pneumonia among cancer patients include the localization of neoplasms in the lungs, head and neck organs, upper gastrointestinal tract, breast, and as well as the presence of signs of emphysema and coronary calcification according to CT data
PATHOLOGICAL PHYSIOLOGY
Aim. To evaluate the effect of etamsylate on the activation of signaling pathways involved in the regulation of platelet aggregation in the setting of macrohematuria following ureteral lithotripsy (ULT).
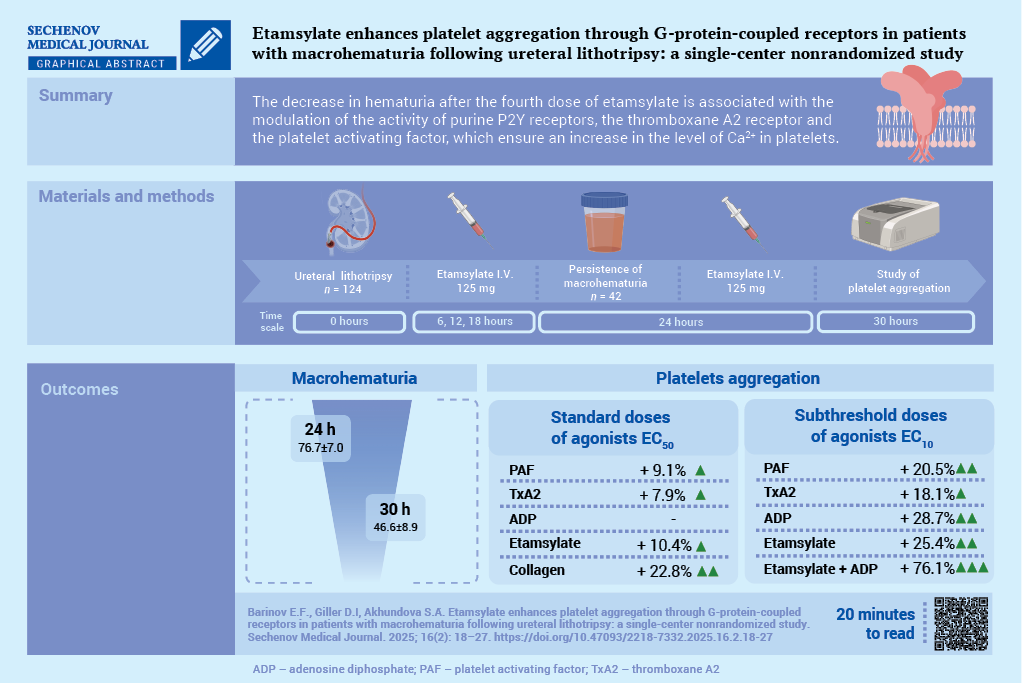
Material and methods. A total of 192 patients undergoing ULT followed by ethamsylate administration were assessed for inclusion in the study. All patients received nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The study included 42 patients (20 men and 22 women; mean age 54.2 ± 15.1 years) who developed macrohematuria following administration of three doses of etamsylate (125 mg I.V. the first dose was administered 6 hours after ULT, followed by further doses every 6 hours). Platelet receptor activity was assessed before and after administration of the fourth dose of ethamsylate (125 mg I.V.) using standard (EC50) and subthreshold (EC10) concentrations of agonists: epinephrine, adenosine triphosphate, adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine, platelet-activating factor (PAF), soluble type IV collagen, and a stable thromboxane A2 analog.
Results. After administration of the fourth dose of etamsylate, macrohematuria significantly decreased compared to baseline values: 46.6 ± 8.9 vs. 76.7 ± 7.0 red blood cells per field of view (p < 0.001). After administration of the fourth dose of etamsylate, upon stimulation with standard agonist concentrations (EC50), there was a significant increase in the activity of the PAF receptor by 9.1% (p = 0.007), the thromboxane prostanoid receptor by 7.9% (p = 0.006), the glycoprotein VI receptor by 22.8% (p < 0.001), and ethamsylate-induced platelet aggregation by 10.4% (p < 0.05). The maximal aggregatory response using subthreshold agonist concentrations (EC10) was observed when platelets were incubated simultaneously with ethamsylate and ADP: amplitude, slope, and AUC (area under the curve) increased by 16.9%, 60.0%, and 54.7%, respectively, compared to isolated stimulation of P2Y receptors (p < 0.05), and by 26.2%, 77.2%, and 65.6%, respectively, compared to incubation with ethamsylate alone (p < 0.05).
Conclusion. The maximal proaggregatory effect of ethamsylate was mediated through P2Y receptors, along with modulation of thromboxane prostanoid and PAF receptors, which promote intracellular Ca²+ elevation
SURGERY
Aim. To evaluate the short-term outcomes of non-operative management (NOM) for blunt splenic trauma and to identify prognostic factors for its success at a tertiary hospital.
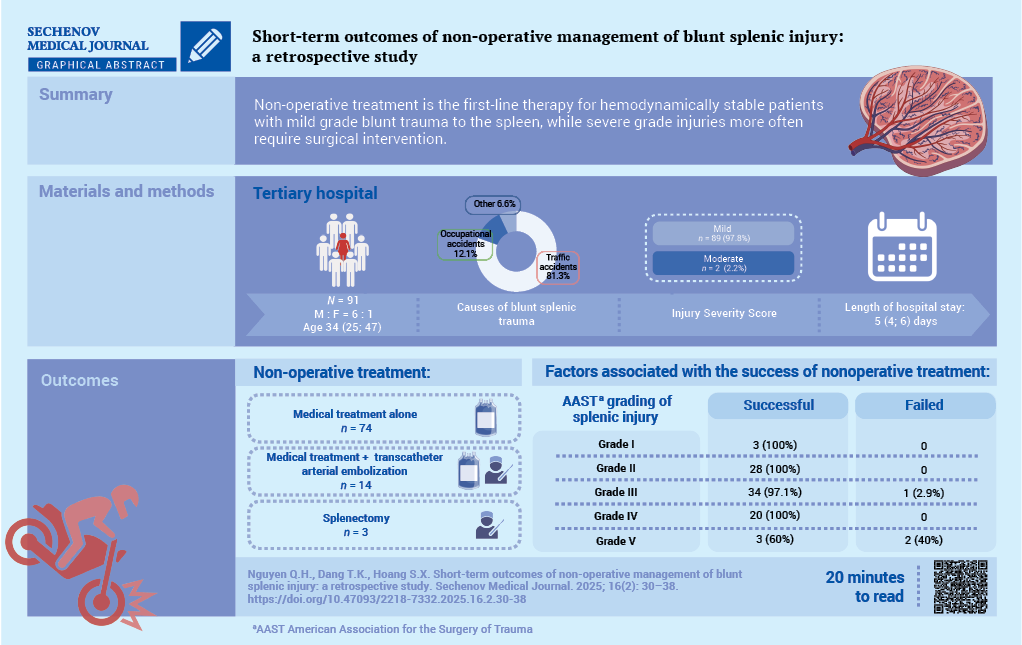
Methods. The study cohort comprised 136 patients with blunt splenic rupture treated at People’s Hospital 115, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, between January 2021 and December 2023. Non-operative management was implemented in 91 cases (66.9%). Collected data included demographics, injury characteristics, therapeutic interventions, complications and NOM outcomes.
Results. Among the 91 patients who received NOM, the median age was 34 (25; 47) years with male-to-female ratio of 6:1. Traffic accidents accounted for most splenic ruptures (81.3%). Clinical symptoms included abdominal pain (98.9%) and distension (27.5%). Abdominal computed tomography findings according to the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) classification revealed predominantly Grade II (30.8%) and Grade III (38.5%) splenic injuries. The hemoperitoneum volume correlated significantly with injury severity (p = 0.029). NOM was successful in 88 patients (96.7%), whereas three patients (3.3%) required splenectomy. The median hospital stay was 5 (4; 6) days. The median amount of blood transfusion was 937.5 ± 340.9 ml. No mortality was reported
Conclusions. Our findings confirm that NOM should be considered as a first-line therapy for hemodynamically stable patients with blunt splenic injury, as it safely obviates the need for surgery while avoiding operation-associated morbidity.
ONCOLOGY
Aim. To evaluate the diagnostic capabilities of combined positron emission tomography (PET) with accumulation of 18-fluorodeoxyglucose and computed tomography (CT) data, with additional 3D-visualization of CT DICOM files using the 3D Slicer software, in detecting tumor invasion of the paragastric tissue in locally advanced gastric cancer.
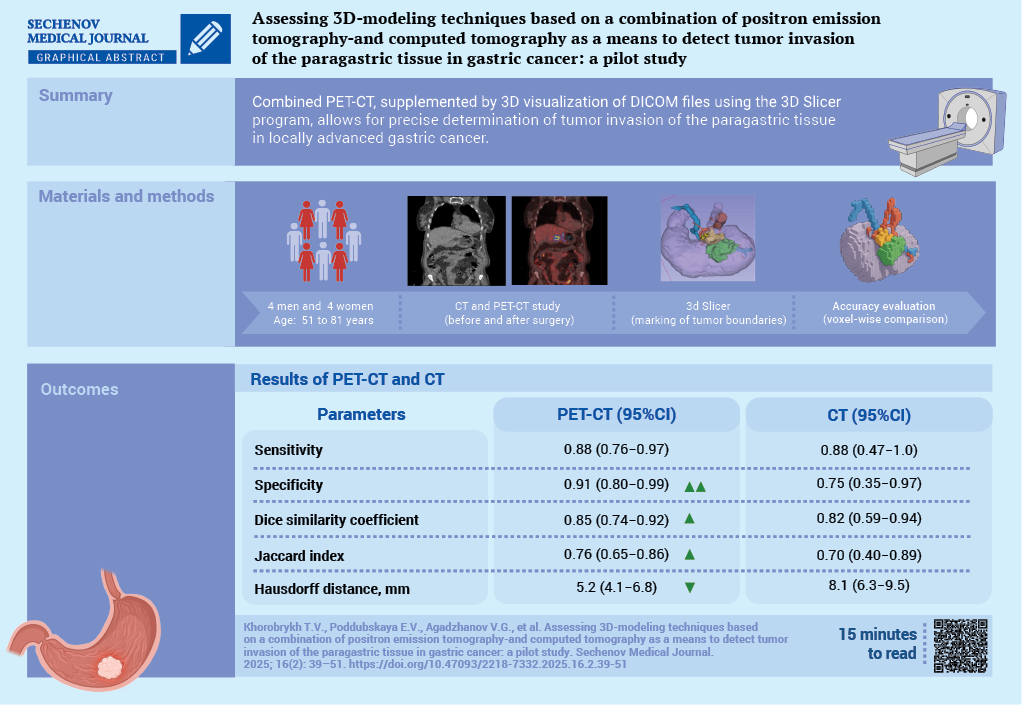
Materials and methods. A prospective open-label study was conducted as part of the research project “SmartGastro”. Four women and four men aged 51 to 81 years with a histologically confirmed diagnosis of gastric cancer underwent combined PET/CT following the “Whole Body” protocol at 60–80 minutes after the administration of the radiopharmaceutical agent (RPA). The obtained results were analyzed through visual assessment of CT and PET images separately, as well as through fused scans, followed by 3D reconstruction based on CT DICOM data. All patients underwent surgery. The resected macroscopic specimen was stepwise excised along its perimeter, followed by a histological examination of the resection margins (paragastric fat tissue). In all cases, R0 resection was confirmed, indicating radical tumor removal. The initial delineation of tumor boundaries based on PET-CT and CT imaging was compared voxel-by-voxel with the secondary delineation performed through a visual assessment of the excised macroscopic specimen.
Results. In 5 out of 8 cases, compromised peritumoral paracardial tissue detected on CT corresponded to regions of radiopharmaceutical agent uptake on PET. Areas demonstrating increased RPA accumulation in the peritumoral tissue, along with a corresponding rise in densitometric values on CT, were indicative of true invasion. This was confirmed by a histological examination of the resected specimen, in 6 out of 8 cases. The sensitivity of combined PET/CT, assessed on a voxel-by-voxel basis against postoperative pathological findings, was 0.88 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.76–0.97), while specificity reached 0.91 (95% CI: 0.80–0.99). The discrepancy in tumor boundaries between these modalities, determined using the Hausdorff distance, was 5.2 mm, with a mean tumor size of 38×30×39 mm. Conclusion. Combined PET/CT enables the surgeon to identify precisely a compromised mesolayer adipose tissue.
The construction of 3D-models of perigastric tissues affected by the tumor process, combined with the visualization of the gastric tumor and associated vasculature, facilitates comprehensive preoperative planning for oncological surgery.
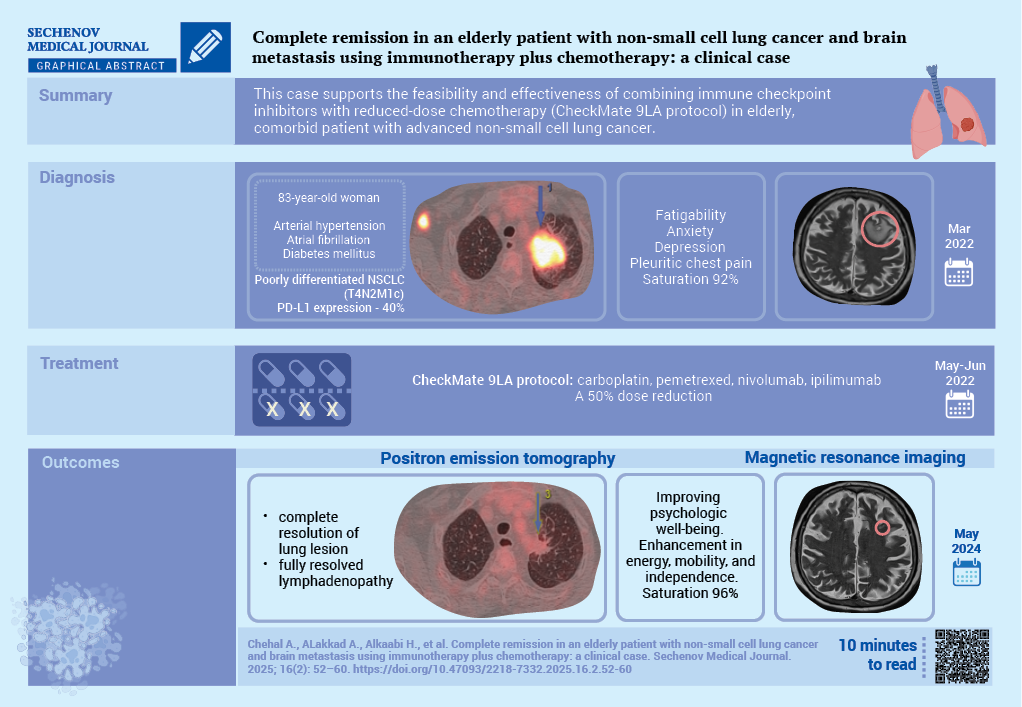
Lung cancer remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality, with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounting for the majority of cases. Among its subtypes, adenocarcinoma is most prevalent. Stage IV NSCLC comes with a poor prognosis, particularly in elderly patients with comorbidities. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) checkpoint inhibitors have demonstrated promising efficacy, including in cases with brain metastases.
Case report. The case concerns an 83-year-old woman with diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, and atrial fibrillation, diagnosed with stage IVB poorly differentiated lung adenocarcinoma which was confirmed by a percutaneous lung biopsy. PD-L1 expression was 40%. Magnetic resonance imaging identified a solitary brain metastasis. The patient was treated with dexamethasone and a CheckMate 9LA protocol was initiated with reduced-dose carboplatin, pemetrexed, nivolumab, and ipilimumab. A two years follow-up positron emission tomography showed a significant reduction in lung cancer. The brain lesions had almost disappeared, and in addition a clinical improvement could be observed.
Discussion. This case underscores the potential for durable remission and improved quality of life through individualized treatment strategies in older patients with advanced NSCLC and brain involvement
ISSN 2658-3348 (Online)